Disaster
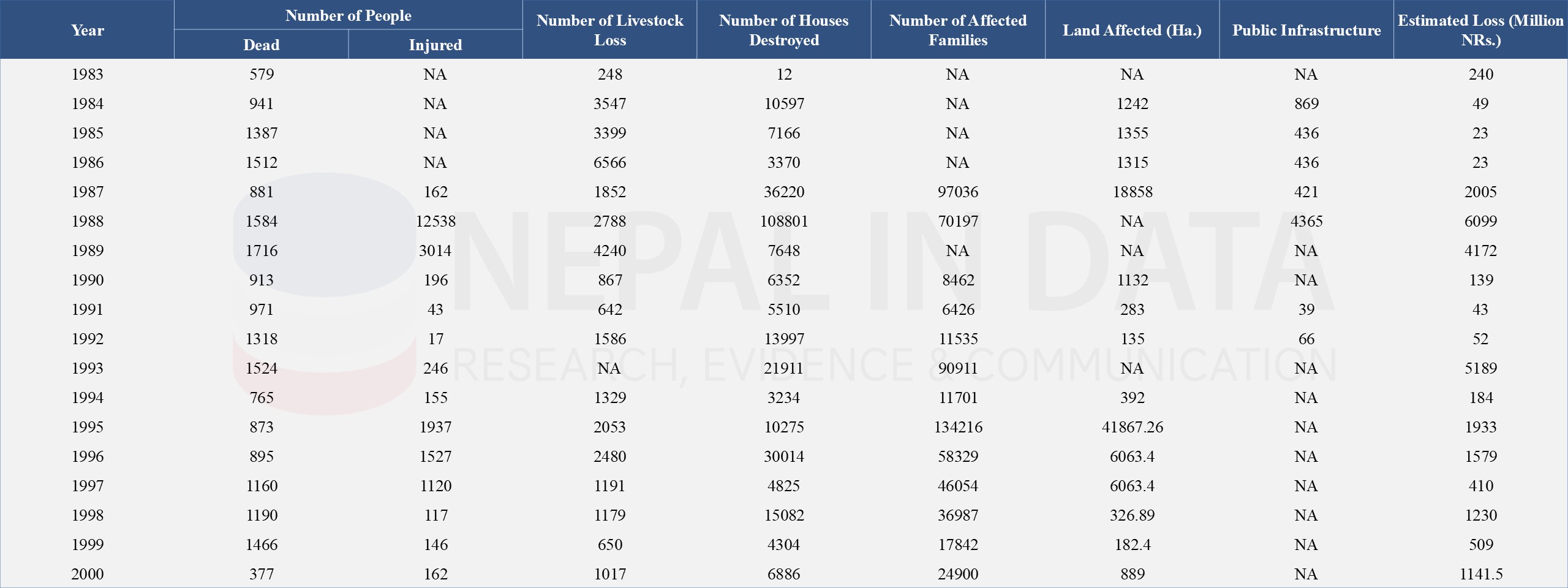
The following Table 1 and Table 2 present the time series data of the loss of lives and property due to disasters from 1983 to 2023. Major peaks of losses are seen in 1988, 1995, 2015, 2017, and 2020 with significant losses in lives, livestock, houses, and economic losses. The highest number of deaths occurred in 2015, with 9,248 casualties due to the major earthquake. Monetary losses vary in different years due to the severity of the disaster. Overall, it reflects the cyclical nature of disasters in Nepal, with certain years marked by catastrophic events leading to extensive damage and loss.
Table 1: Loss of Lives, Livestock, and Other Effects by Type of Disaster in Nepal from 1983 - 2000
(Disasters: Flood, Cold, Landslide, Avalanches, Earthquake, Fire, Epidemic, Windstorm, Hailstone &Thunderbolt)
Source: Nepal Disaster Risk Reduction Portal (drrportal.gov.np)
Table 2: Loss of Lives, Livestock, and Other Effects by Type of Disaster in Nepal from 2001 - 2023
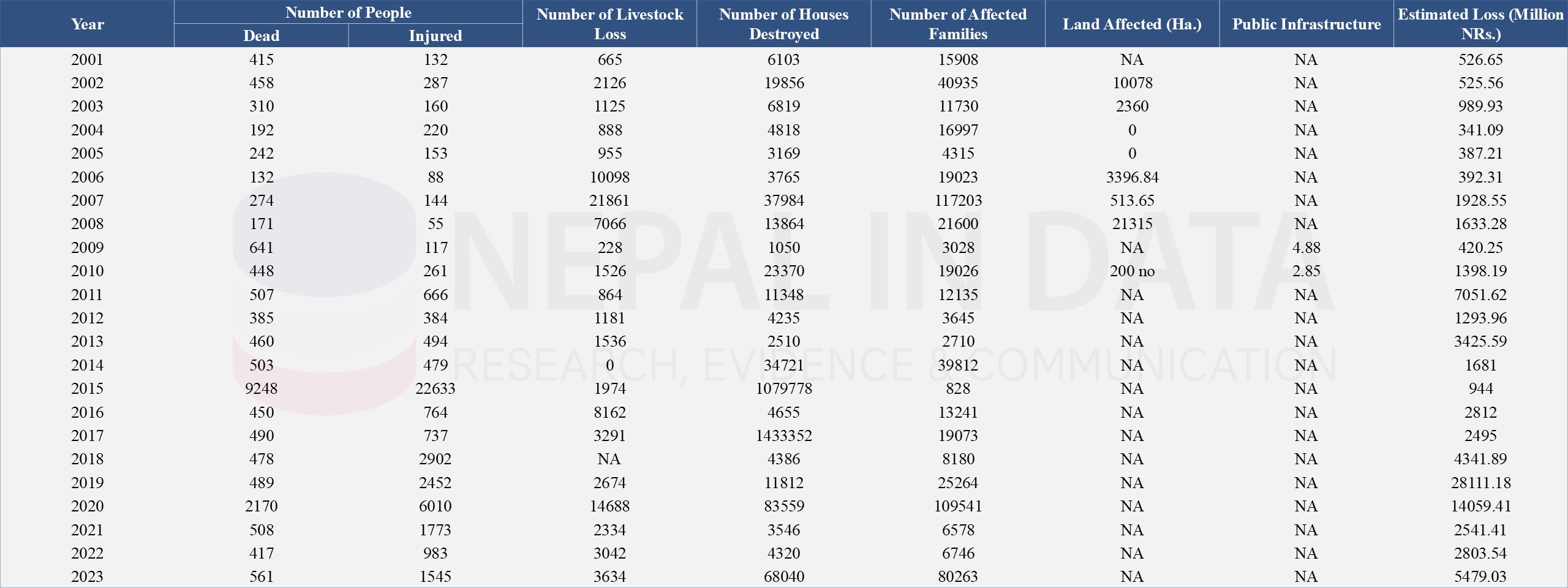
Table 3 shows the major disasters that happened in Nepal from 2016 to 2023 and the loss of lives and property due to these incidents. The data presents that landslides, fires, and floods are major hazards, resulting in significant casualties and damage. To mitigate the impact of Nepal's various hazards, it is necessary to improve the early warning system, strengthen community resilience, encourage climate adaptation, and enforce building safety laws.
Table 3: Major Disaster in Nepal and the Damage and Loss, 2016 - 2023
Source: Nepal Disaster Risk Reduction Portal (drrportal.gov.np)
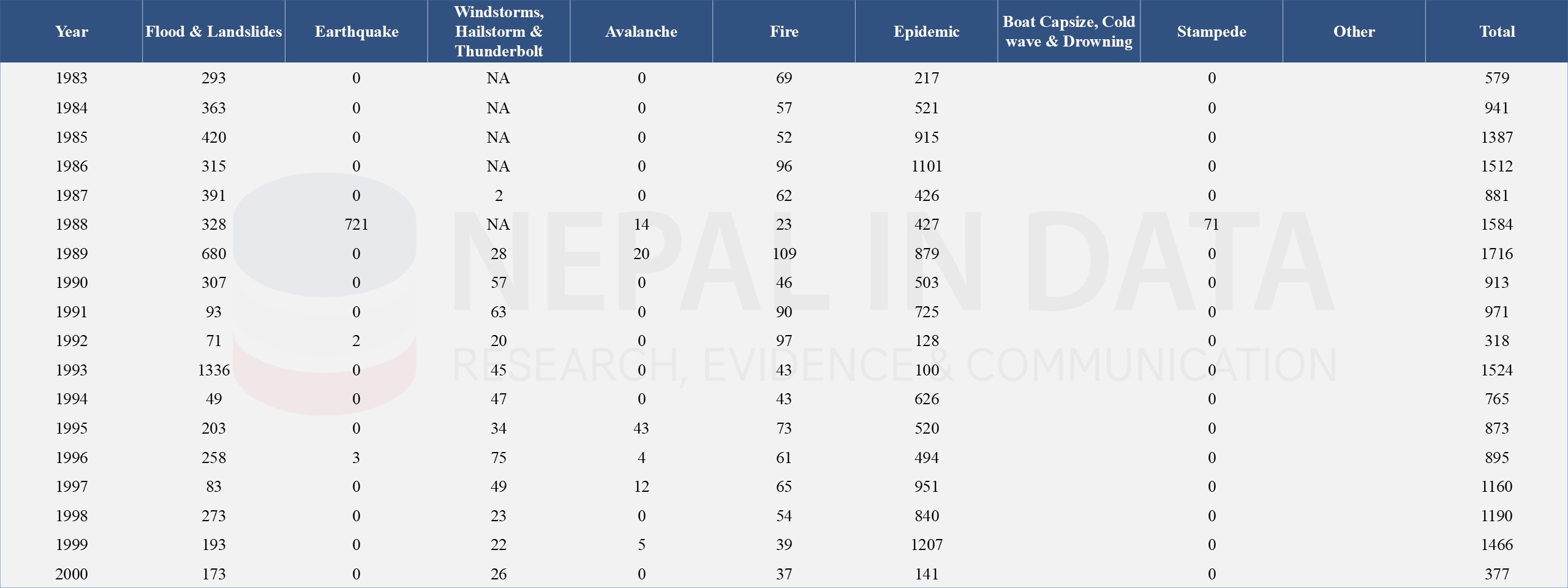
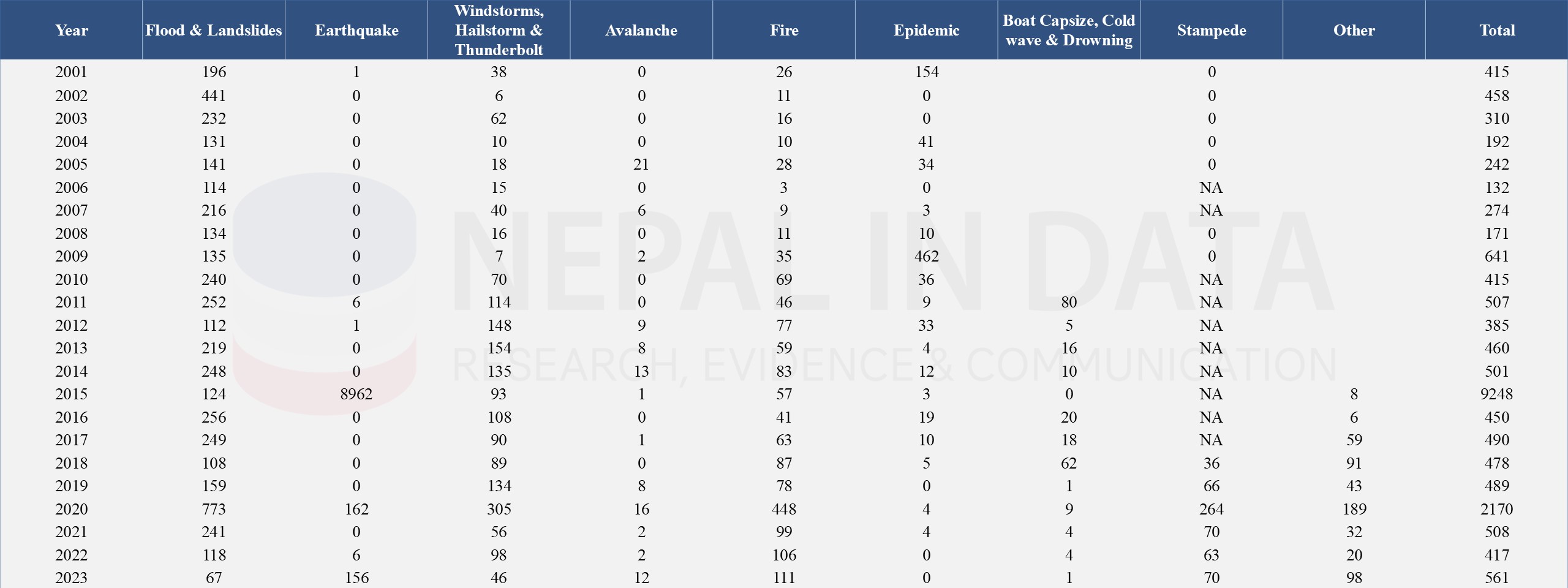
The following Table 4 and Table 5 shows the number of human causalities from different disasters in Nepal from 1983 to 2023. Floods and landslides have consistently contributed to a significant number of casualties. A major earthquake occurred in 2015, leading to a significant loss of life. The government should focus on community-based preparedness and response programs and enforce strict building codes for seismic resilience, especially in earthquake-prone areas.
Table 4: Human Casualties Due to Major Disasters in Nepal from 1983 - 2000
Source: Nepal Disaster Risk Reduction Portal (drrportal.gov.np)
Table 5: Human Casualties Due to Major Disasters in Nepal from 2001 - 2023
Climate Induced Disaster
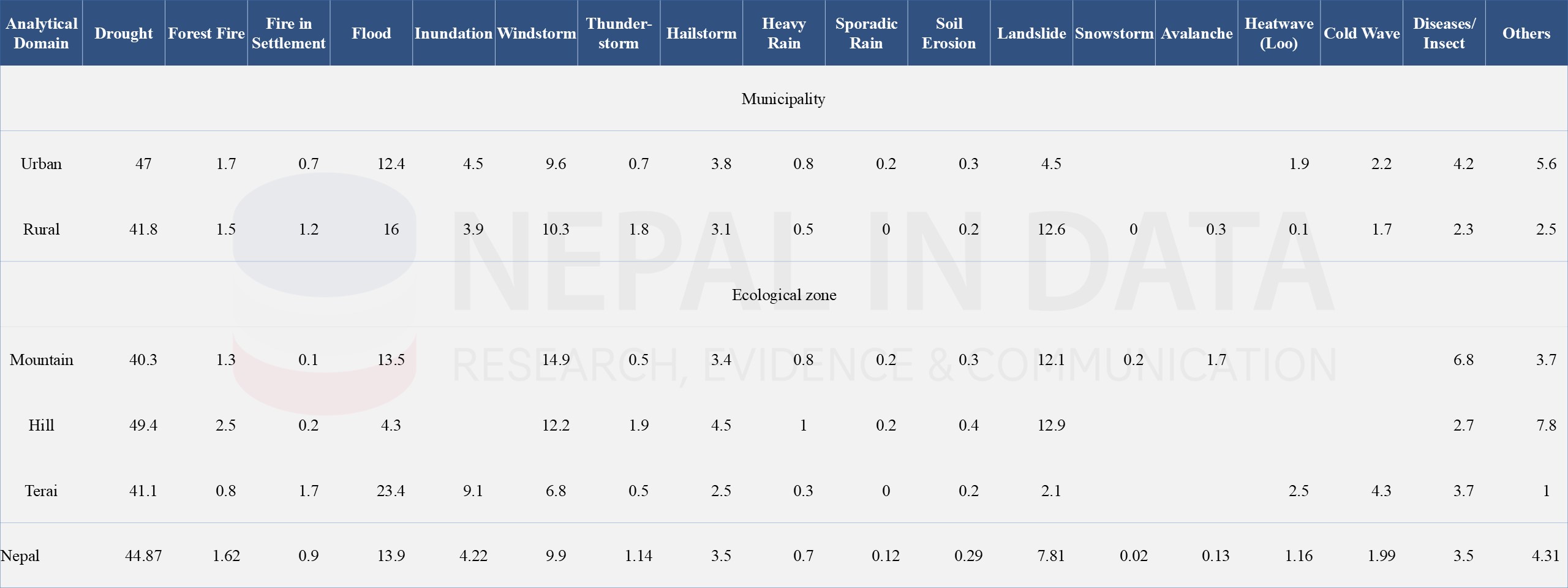
The following Table 6 and Table 7 provide the major climate-induced incidents reported by the household. Over the past 25 years, Nepal has been suffering from various ranges of natural disasters, showing insignificant patterns in disaster incidence. Drought has been a major disaster imposing an extensive impact on communities nationwide. The incidence of flood was significantly observed in the Terai region. This result highlights the need for specific disaster preparedness and response strategies to address the different challenges faced at the community level.
Table 6: Households (%) Reporting Major Climate Induced Incidences During Past 25 Years, 2022
Source: National Climate Change Survey,2022, National Statistics Office (NSO)
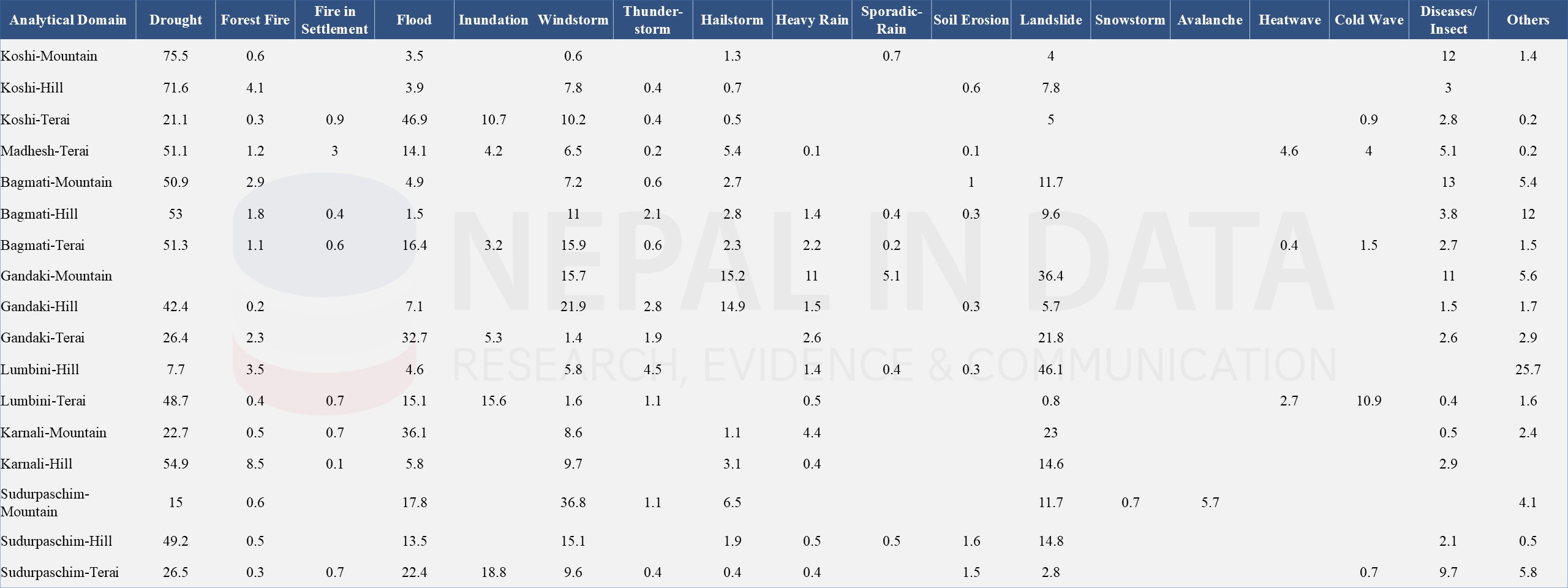
Table 7: Households (%) Reporting Major Climate Induced Incidences in Different Minor Ecological Belts During Past 25 Years, 2022
Source: National Climate Change Survey,2022, National Statistics Office (NSO)
The following Table 8 presents the level of impact from various climate-induced disasters over the past 25 years, categorized into different impact severity levels. Drought has been a significant and recurring disaster, with different degrees of impact. The data highlights the need for individual mitigation and adaptation strategies, considering the varying impact levels across different climate-induced disasters.
Table 8: Level of Impact (%) from the Climate Induced Disaster Over the Past 25 Years, 2022
Source: National Climate Change Survey 2022, National Statistics Office (NSO)
Table 9 provides information on the percentage of affected households from various climate-induced disasters over the last 25 years. Drought is the major disaster followed by diseases/insects. The data shows the patterns of climate-induced disasters that individual households face and need inclusive strategies to mitigate and cope with those challenges.
Table 9: Households (%) Affected by Climate Induced Disasters in the Last 5 Years, 2022
Source: National Climate Change Survey,2022, National Statistics Office (NSO)
Table 10 shows the percentage distribution of households facing economic losses categorized by specific disasters in Nepal over the last five years. Fire(settlements), floods, inundations, and landslides are catastrophic, leading to economic losses exceeding NPR 60,000 for a significant majority of households. Effective disaster management policies are essential for reducing economic losses in Nepal by focusing on high-risk areas and enhancing community awareness and preparedness programs.
Table 10: Percentage of Households with Economic Loss Due to Climate-Induced Disasters in the Last Five Years, 2022
Source: National Climate Change Survey,2022, National Statistics Office (NSO)
Ward-Based Disaster Risk Situation
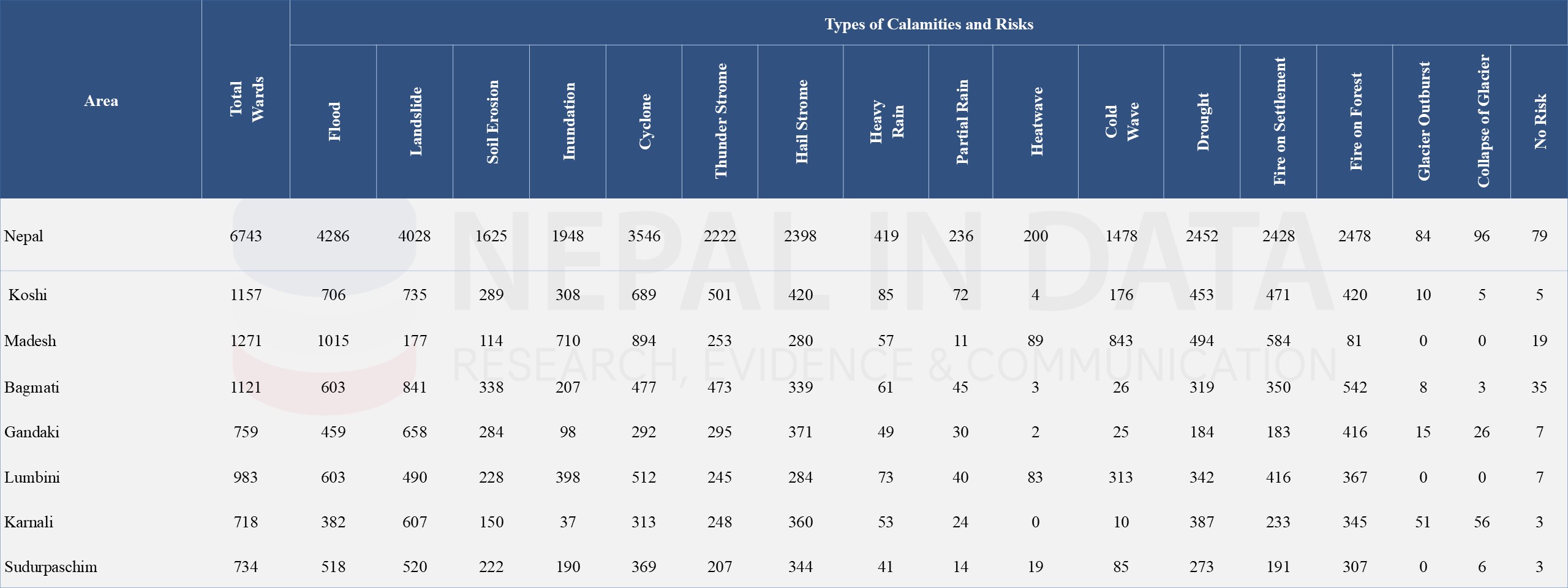
The community questionnaire from the Population Census 2021 collected data on sixteen types of natural disasters/hazards across the 6743 wards in Nepal. It revealed that 6664 wards (99 %) have some risk. The most common hazards are floods in 63.6 percent of wards and landslides in 59.7 percent of wards respectively. Wards in Koshi, Bagmati, Gandaki, Karnali, and Sudurpaschim provinces show a high prevalence of landslide risk while wards in the Madhesh and Lumbini provinces show a higher prevalence risk of flooding.
Table 11: Wards Based on Disaster Risk Situation, 2021
Key Takeaways
Nepal is a disaster-prone country due to its topography and climatic conditions. Earthquakes, landslides, floods, drought, fire, and thunderbolts are the major causes of disaster events. Environmental degradation and climate change are assisting in the occurrence of natural hazard events causing yearly loss of life, property, and a significant proportion of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) due to disaster. Poor, Indigenous marginalized, women, girls, children, disabled, and elderly groups are mostly impacted by disasters. It is needed to strengthen institutional frameworks and integrate Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) into national and local development planning are essential to mitigate risks due to natural hazards and human induced disasters.